Sanjeet Kumar
Ravenshaw University
sanjeet.biotech@gmail.com
Ravenshaw University
sanjeet.biotech@gmail.com
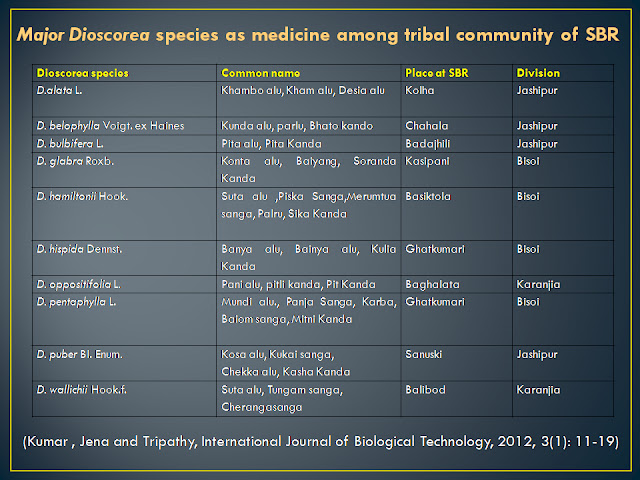
Research in Dioscorea species
Various researchers such as Sinha and Lakra (2005), Edison et al.(2006), Mishra
et al. (2007), Prusti and Behera (2007), Swarnkar and Katewa (2008), Sahu et
al.(2010), Kumar et al. (2010), Namrata et al. (2011) provided ethno-botanical
reports on Dioscorea species which
state that it is used as a food
among tribal communities of Orissa in critical time. Tubers of Dioscorea oppositifolia is used in the
treatment of swellings, scorpion and snake bites, juice of Dioscorea wallichi
is used in the treatment of Jaundice, Dioscorea
hispida is used as an antidote in arrow poison. Dioscorea species to the food security among tribes of Jeypore
tract, Orissa. Tubers of Dioscorea
bulbifera are eaten after prolonged boiling in Malkangiri District of
Orissa, used as contraceptive, used against cough, Leprosy, Diabetes,
Spermoitic, aphrodisiac and antihelmintic and also against rheumatism (in
Deogard district of Odisha), piles, dysentery, syphilis and ulcers. Dioscorea pentaphylla is used against
abdominal pain after delivery.Chandra et al., 2012 reported the nutritive and
phytochemicals present in Dioscorea
deltoidea of Garhwal Himalaya. Several authors
reported pharmacological activity of Dioscorea.among
them are Ahmed et al. (2009), Rani et al. (2010), Murthy et al. (2011), Suresh
et al. (2011), Suriyavathana and Indupriya (2011), Ghosh et al. (2012). They reported
that Dioscorea bulbifera inhibits the
α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity which is responsible for its anti-diabetic
action. It has anti-oxidant, anti-hyperglycemic and anti-dyslipidemic
activities. Methanol extract of Dioscorea
oppositifolia has anti-ulcer activity. Ethanolic leaf extracts of Dioscorea hispida have anti-inflammatory,
analgesic and anthelmintic activity. Nutritional values of Dioscorea pentaphylla, Dioscorea oppositifolia, Dioscorea tomentosa and Dioscorea spicta have been reported by
Mohan and Kalidas, 2010.
Behera et al., 2010 reported the concentration of an
active compound Diosgenin and ascorbic acid of the tubers of Dioscorea species found in Orissa. Mohan
and Kalidas, 2010 reported the anti-nutritional compounds as Tannin, Hydrogen
cyanide and Oxalate. Prakash and
Hosetti, 2010 reported the anti-bacterial activity against S.aureus, P.aeruginosa and K.pneumoniae and anti-fungal against T.rubrum, M.gypseum, T.tonsurans,
M.audouini and C. albicans of
Dioscorea pentaphylla of mid Western Ghats. In 2005, Pérez et al. reported that Dioscorea species is used in gastritis
among Yoruba Tribal groups of Cuba. Lila (2009) reported that crushed tubers of
Dioscorea hamiltonii are given as
body refrigerant during summer and also used in Diarrhoea, sap of tubers of Dioscorea hispida is used against
Harinad( peeling of skin of feet), Dioscorea
bulbifera is used against Tuberculosis, raw tuber of Dioscorea pentaphylla is used against Diphtheria in Cattle. In
2011, Danikou et al. reported that tubers of Dioscorea bulbifera are used as food plants in Bénin.Webster et al.,
1984 reported the component Diobulbin D in Dioscorea
bulbifera and Dioscorea hispida
of Thailand which is responsible for their bitterness. Yoon et al., 2008
reported a bioactive compound Allantoin in Dioscorea
rhizomes. Bhandari and Kawabata, 2005 identified bitter components as Furanoid
norditerpenes cyanogens content. Martin
et al., 1974 reported the yellow pigments of Dioscorea bulbifera, the major part of the yellow color is due to
the presence of saponifiable easters of xanthophylls such as Lutein. Olayemi
and Ajaiyeoba, 2007 reported the anti-inflammatory activity of Dioscorea esculenta. Theersin and Baker,
2009 identified phenolic compounds and analyzed the antioxidant potential of Dioscorea hispida. The Anti-clastogenic
effect of aqueous extract of Dioscorea
alata was reported by L. Wang et al. in 2011.
Mbiantcha et al., 2011 reported
the analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties of extract from the bulbils of Dioscorea bulbifera. In 2003, Mignouna and Dansi documented the domestication of Dioscorea species by the Nago and Fon
ethnic groups in Benin. Kouakou et al., 2010 reported biochemical parameters of
Dioscorea alata and Dioscorea rotundata during post harvest
storage. Otegbayo et al., 2011 reported the physiochemical properties of yam
Starch and effect on textural quality on food product. Marie et al., 2005
reported the anti-nutritional factors as Saponin, total phenol and tannin of
selected Dioscorea species of
Jamaica. Ogbuagu, 2008 reported the nutritive and anti-nutritive values of
Dioscorea bulbifera and Dioscorea
dumentorum. They also reported the presence of alkaloids, oxalate and
saponin at high concentration are responsible for the qualification of the
species as Wild (Bitter) and inedible. Polycarp et al., 2012 characterized the
chemical and anti-nutritional factors as oxalates, tannin and phytates of
Ghana.







No comments:
Post a Comment