A. Behera & Sanjeet
sanjeet.biotech@gmail.com
Introduction
Millions of people in many developing countries do not get enough food to meet their daily requirement and many more suffer deficiency of micronutrients. The rural and tribal communities even today depend on wild resources including wild edible tuber(s) to meet their daily food requirement and more particularly during the period of food crisis. The value of wild edible plants in food security has not been given sufficient attention in India and particularly in Odisha. During last few years some attempt has been made to document the rich indigenous knowledge on the medicinal use of wild plants but socio-economic, traditional nutritional aspect of wild food plants still lack adequate attention. There are about 1532 edible wild food species available in India mostly in Eastern Ghats, Western Ghats and Himalayan Hill ranges (Reddy et al., 2007). Tubers play a major role in supplementing staples foods with micronutrients and can constitute a “Safety Net” during the period of food shortage (Chattopadhyay et al., 2010). Knowledge on wild tubers is gradually declining and even disappearing with increased modernization and migration to urban area due to poverty and other socio-economic factors. Documentation and revalorisation indigenous knowledge on wild tubers is urgently needed to promote nutritional health of the local inhabitants and to conserve genetic and cultural diversity as well. Almost all tribal groups of Odisha have been using Amorphophallus species (Oluā) as a food that are generally taken as vegetables and used as medicine in different formulations. Amorphophallus tubers (corms) constitute an economically important staple food and medicine for millions of people in the world (Sen et al.,1995).
Ethnobotanical Values
Amorphophallus are long been used in China, Japan and South East Asia as a food source and traditional medicine. In traditional Chinese medicine (Tem), a gel prepared from the flower has been used for detoxification, tumour- suppression, blood stasis alleviation and phlegm liquefaction and for treatment of asthma, cough, hernia, breast pain, burns as well as haematological and skin disorders (Chua et al., 2010). Amorphophallus campanulatus tuber is used for the treatment of enlarged spleen, rheumatism and tumour (Tripathi et al., 2010). The tubers are known to treat stomach ailments, has medicinal properties against fever, swelling, diarrhoea, used in piles and given as restorative in dyspepsia enlargement, asthma and rheumatism. Rhizomes are used for boils and opthalmia, also as an emmenagogue. Petioles used in scorpion bites, dysmenorrhea and are applied externally as an irritant to treat rheumatism (Hasan et al., 2009). Corms are also used in case of ear aches, swelling of throat, pimples, intereostal neuralagia, fever and also useful in cases of elephantiasis, tumours, inflammations, constipation, seminal weakness, fatigue, anaemia and general disability (Ravi et al., 2009).
Pharmacological Activity
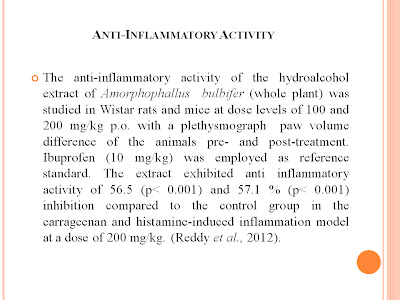
Anti-Inflammatory Activity
Antioxidant activity of methanolic and aqueous extract of Amorphophallus campanulatus tuber was studied for its free radical scavenging property (Sahu et al., 2009). The anti-inflammatory activity of the hydroalcohol extract of Amorphophallus bulbifer (whole plant) was studied in Wistar rats and mice at dose levels of 100 and 200 mg/kg p.o. with a plethysmograph paw volume difference of the animals pre- and post-treatment. Ibuprofen (10 mg/kg) was employed as reference standard. The extract exhibited anti-inflammatory activity of 56.5 (p< 0.001) and 57.1 % (p< 0.001) inhibition compared to the control group in the carrageenan and histamine-induced inflammation model at a dose of 200 mg/kg (Reddy et al., 2012).
Analgesic Activity
Analgesic activity in Amorphophallus bulbifer (whole plant) was evaluated using tail flick and tail immersion techniques by measuring the reaction time of the animals (rats) treated with either standard or extract. Pentazocin (30 mg/kg) was used as reference which showed significant anti-inflammatory at the two test dose levels at the 4th hour (p< 0.001). The extract showed reaction times of 7.33 (p< 0.001) and 7.83 (p< 0.001) min in the tail flick and tail immersion models at a dose of 200 mg/kg while the normal and reference groups exhibited reaction times of 2.16, 2.66 and 8.16 (p< 0.001) and 8.5 (p< 0.001) in the tail flick and tail immersion methods, respectively, this lends some support for its use in traditional medical practice (Reddy et al., 2012).
Anti-Cancer Activities
Epidemiological evidence suggests that dietary factors play an important role in human health and in the treatment of certain chronic diseases including cancer (Trichopoulos et al., 1996). Some dietary sources of Amorphophallus species contain anti - tumour compounds and such compound are candidates for chemo preventive agents against cancer development (Dorai et al., 2004). The anticancer property of nutrients derived from plants as well as non - nutritive plant derived constituents have been proved indifferent in vitro and in vivo models , which has led to an increased emphasis on cancer prevention strategies in which these dietary factors are utilised (Barnes et al.,1995). Epidemiological evidence suggests that dietary factors play an important role in human health and in the treatment of certain chronic diseases including cancer (Madhurima et al., 2012). Amorphophallus campanulatus has anticancer properties (Madhuri et al., 2008). Antioxidant and anti- tumor activity of ethanolic extract of Amorphophallus paeonifolius tubers against 7,12- dimethyl benz (a) anthracene (DMBA) induced mammary tumour in rats were studied in-vitro and in-vivo methods and the plant extract was evaluated for mammary tumour activity by chemical induced tumour. The results showed total flavanoids compound in ethanolic tuber extract of Amorphophallus paeonifolius was found to be 8.8 g/100g calculated as Quercetin equivalent, effect of ethanolic extract on RBC, WBC, Hb & Neutrophils as a-P< 0.001,b-P<0.01,c-P<0.05, ns-non significant, effect of AP-extract on tumor latency and tumour burden were found as extremely significant at P<0.001. One-way ANOVA Tukey method was followed for statistics. It was concluded that ethanolic extract of Amorphophallus paeonifolius has shown significant antitumor and antioxidant effect in animals. The flavonoid in tuber extract of Amorphophallus paeoniifolius showed significant antitumour and antioxidant effect (Jagatheesh et al., 2010).
Hepatoprotective Properties
The pretreatment with dried tuber of Amorphophallus campanulatus (MAC) reduced the biochemical markers of hepatic injury like serum glutamate pyruvate transaminase (SGPT), serum oxaloacetate transaminase (SGOT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), bilirubin (BRN) and total protein shows hepatoprotective activity. There is increase in the levels of superoxide dismutase (SOD), Catalase (CAT), and glutathion peroxidise (GPx) shows that the plant may possess hepatoprotective and antioxidant property (Singh et al., 2011). The hepatoprotective activity of methanol and aqueous extracts of Amorphophallus paeoniifolius tubers was confirmed against paracetamol induced liver damage in rats which was induced by paracetamol. The phytochemical investigation of the extracts showed presence of carbohydrates, proteins, steroids and flavonoids. Pre-treatment of the rats with methanol and aqueous extract prior to paracetamol administration caused a significant reduction in the values of sGOT, sGPT, sALP and sB (P<0.01) almost comparable to the silymarin and Liv-52. Thus was confirmed by histopathological examination of the liver tissue of control and treated animals (Hurkadale et al., 2012).
Anti-bacterial Activity
The flavonoid, 3,5-diacetyltambulin isolated from Amorphophallus campanulatus was studied for in-vitro antibacterial, antifungal and cytotoxic activities which showed significant antibacterial activites against four gram positive bacteria (Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus megaterium, Staphylloccous aureus, Streptococcus β – hemolyticus ) and six gram negative bacteria (Escherichia coli, Shigella dysenteria, Shigella sonnei, Shigella flerneri, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Salmonella typhii). The MIC values against these bacteria ranged from 8 to 64 μg/ml but had weak antifungal activity against a number of fungi. In cytotoxicity determination, LC50 of the compound against brine shrimp nauplii was 10.02 μg/ml (Khan et al., 2009). The aqueous and methanolic extracts of spinach (Spinacea oleracia), pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo), suran (Amorphophalus campanulatus) and ghuiya (Colocasia esculenta) were evaluated for antimicrobial activity against bacterial strains (Bacillus cereus, Bacillus subtilis, Escherichia coli, Enterobacter aerogenes, Enterobacter agglomerans, Salmonella enteritidis, Salmonella cholerasius, Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Candida albicans, Penicillium chrysogenum, Enterobacter faecalis, Klebsiella pneumonia, B.sphericus, B.thruengiensis and Cryptococcus meningitis and was performed by Agar well diffusion method on Nutrient Agar medium and Muller Hinton Agar medium. The methanolic extracts of all the vegetables showed moderate to high activity against all the investigated microbial strains (Dubey et al., 2010). The Amorphophallus species showed remarkable antibacterial activity against gram positive (Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus) gram negative (E. coli, P. aeruginosa ) bacteria and antifungal test showed significant activity of Candida albicans (Maharajan et al.,2012).
Antifungal Activity
The complete genome sequence of Bacillus subtilis strain BSn5, isolated from Amorphophallus species, calli tissue show strong inhibitory activity to Erwinia carotovora subsps- carotovora, which causes Amorphophallus soft rot disease and affects the industry development of this organism (Deng et al., 2011). Amorphophallus campanulatus showed good antifungal activity against Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus nizer and Rhizopus aryzae (Khan et al.,2008).
Anti-Diabetic Activities
The Amorphophallus species can be used as anti-diabetic agent (Li et al., 2004). The effect of the acetone extract of elephant-foot yam (Amorphophallus paeoniifolious Dennst.) at 0.1 and 0.25% in the diet of streptozotocin-induced male Wistar diabetic rats was studied which involved a comparison between control and diabetic groups: starch-fed control/diabetic (SFC/SFD), 0.1% acetone extract fed control/diabetic (AEFC0.1/AEFD0.1), 0.25% acetone extract fed control/diabetic (AEFC0.25/AEFD0.25) and aminoguanidine fed control/diabetic (AFC/AFD). The rats were examined for water intake, diet intake, urine output, gain in body weight, urine sugar, fasting blood sugar (FBS) and glomerular filtration rate (GFR). A concentration-dependent amelioration of the diabetic status was observed with respect to all the above studied parameters. FBS of AEFD0.1 and AEFD0.25 groups showed a 23% and 37% reduction, respectively whereas the AFD group showed a 45% reduction relative to the SFD group. The GFR of experimental rats in AEFD0.1 and AEFD0.25 groups showed a 28% and 41% reduction, respectively whereas the AFD group showed a 54% reduction compared to the SFD group which clearly indicate that the acetone extract of elephant foot yam is an effective for streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats (Arva et al., 2012).
Immunomodulatory Activity
Amorphophallus campanulatus tuber is used for the treatment of enlarged spleen, rheumatism and tumour. The effect of the methanol extract (ME) of Amorphophallus campanulatus tuber on immunological function in mice was studied using charcoal clearance, spleen index and delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) response models. The extract was administered orally at doses of 250 and 500 mg/kg, thus exhibited immunomodulatory activity by causing a significant decrease in charcoal clearance, spleen index and delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) response (Tripathi et al., 2010).
Anti-helminthic Activity
Corm was extracted with petroleum ether, chloroform and methanol. Crude tannins were isolated from methanol extract. The extracts and crude tannins were evaluated for anthelmintic activity. Chloroform, methanol extracts and crude tannins showed very good anti-helmintic activity (Ramalingham et al., 2010).
Toxicity
The cytotoxic property of different solvent extracts of Amorphophallus paeoniifolius tuber using Allium cepa L. root tip cells and HEp-2 cell line as two model in vitro systems. The seven extracts of Amorphophallus tuber were tested; the mitotic index and cytotic index were found to be high in petroleum ether and ethanol fractions. The magnitude of cytotoxicity displayed a dose dependent antiproliferative activity on HEp-2 cells which confirms the cytotoxic property (Angayarkanni et al., 2007).